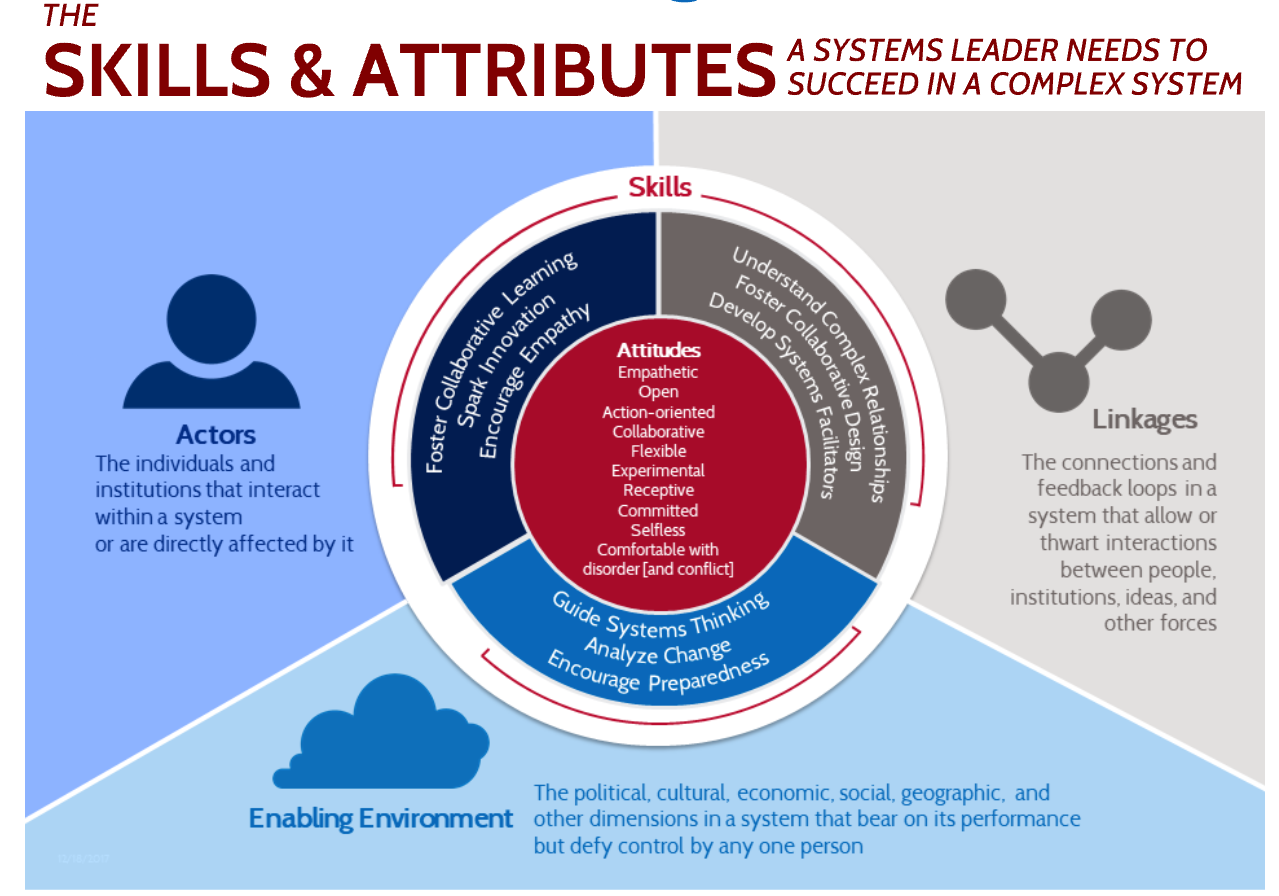
Systems thinking and change
As Fritjof Capra says: a machine can be controlled, a living system can only be disturbed. At best, we will find ways of carefully nudging a living system. According to Donella Meadows, we must find its leverage points, those pivots that allow us to influence system behavior. Most importantly: after each cautious inter- vention, we must patiently... See more
Understanding Living Systems
Celebrating systems thinking through student projects
blog.kumu.io
Buenos ejemplos de mapas
Consider a huge bathtub with slow in and outflows. Now think about a small one with very fast flows. That’s the difference between a lake and a river.
donellameadows.org • Leverage Points: Places to Intervene in a System
We are moving to new definitions of success for organisations & systems, saysIndy Johar. | Helen Bevan | 74 comments
Helen Bevanlinkedin.com
Feedback loop: I’ve Been Using the Wrong Tool for Thinking about the Future
Miguel Pantaleonmedium.com
Vol. 5 No. 1 (2025): Special Themed Issue: Social Presencing Theater | Journal of Awareness-Based Systems Change
Eva Pomeroyjabsc.org