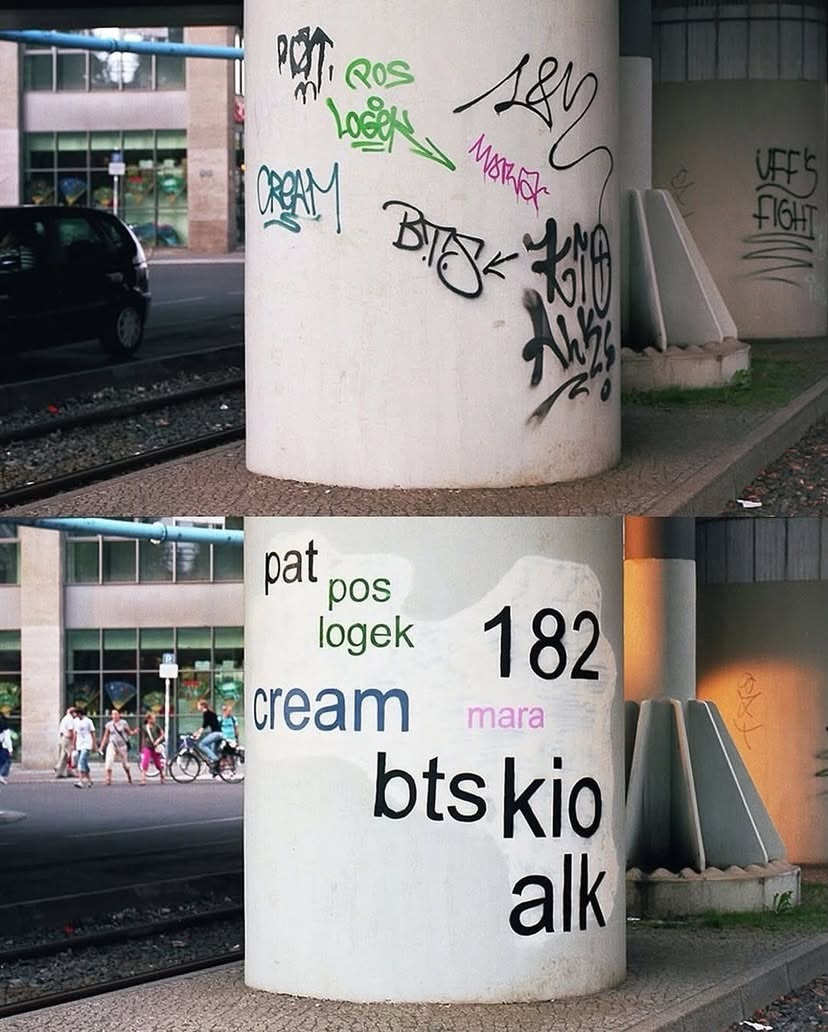Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas
don’t know how else to explain it except to say that when I make time to read, my capacity to deal with my own life — and my own bullshit — expands . My natural tendency to be tightly wound loosens its grip.
Reading as a default state
Think like a gardener, not an architect: design beginnings, not endings.
Unfinished = fertile
“The theater critic Kenneth Tynan once said, “A critic is a man who knows the way, but cannot drive a car.”
― Keith McNally, I Regret Almost Everything: A Memoir
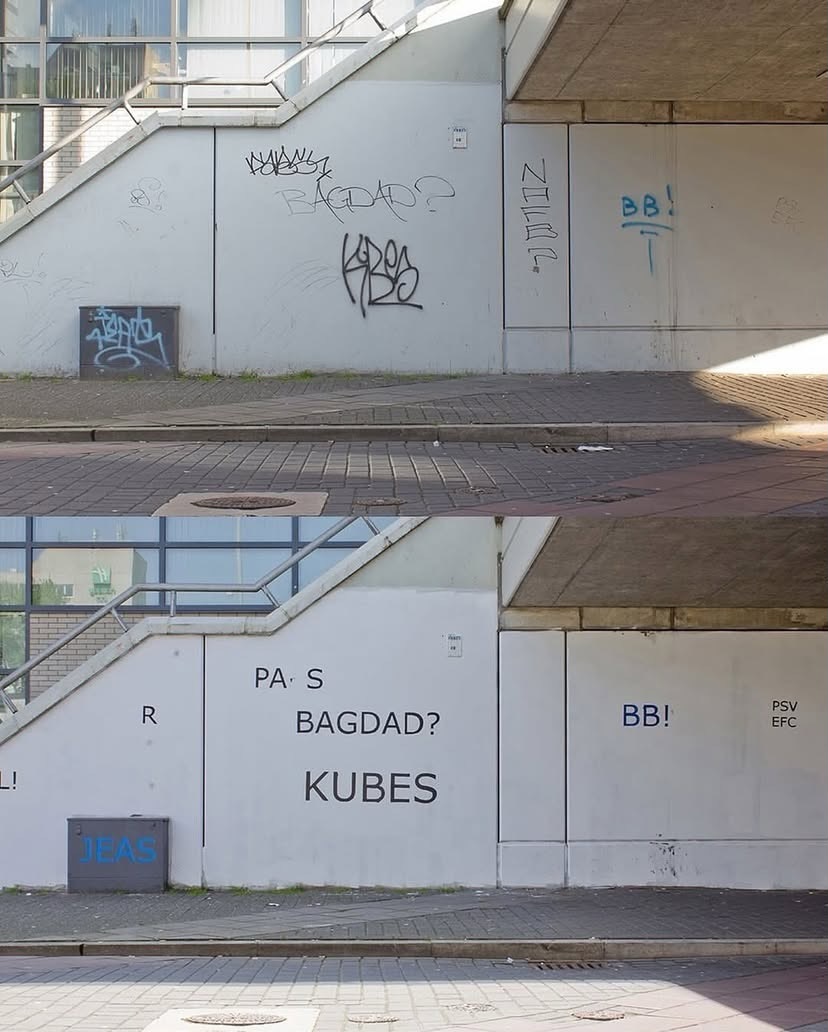
French artist Mathieu Tremblin is known for a project called Tag Clouds, started in the early 2010s, where he intervenes directly on existing graffiti tags in public space.
Tremblin often uses neutral, default typefaces associated with digital interfaces. The city becomes filled with readable signatures that were... See more
therealnurtleinstagram.comWe’ve turned the internet into a vending machine. Push a button, get the Coke. If it doesn’t spit it out fast enough, beat the living shit out of it until it gives you two cokes. Instead, rabbit holing retrains both your curiosity and your patience. It reminds you the internet is more like a labyrinth, and the labyrinth rewards wanderers.
✧ brooklyn 𓆏 • how to use the internet again: a curriculum
37signals Isn't Smarter Than You, But They Are Different
nateberkopec.comEverybody wants to have a village, but few are willing to be villagers. Building presence takes work. It requires vulnerability, patience, and the willingness to show up even when the room is not full. That might mean hosting an event for ten people when you have ten thousand followers. The cost of community is inconvenience.