Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas

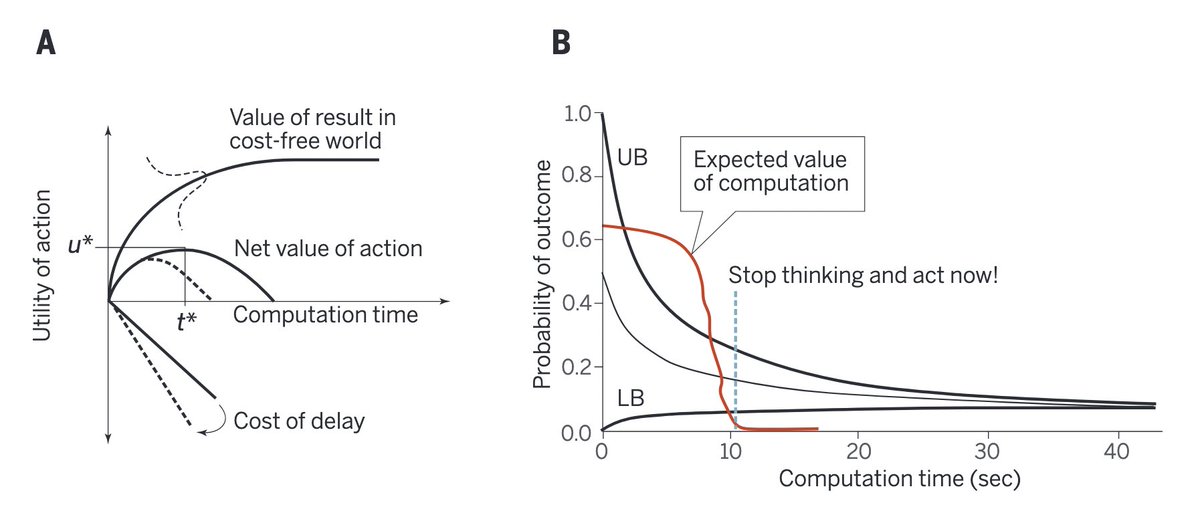
This diagram got me much closer to real life:
The universe has a tax on deliberation.
Rationality collapses into "just do things" quickly.
In a live environment, thinking is not free; every extra second spent optimizing carries opportunity cost, the cost of delay. So while additional... See more
Decision-making as the core of creative practice and entrepreneurship, blurring boundaries between art, business, agency, and personal choice.
TRANSCRIPT
So, yeah, I mean, the way that Yatu and Norm approach their practice and, like, how it sort of, like, blurs this line between art and business, I think is, like, a perfect example of, like, they're just making decisions.
You know, they're like focusing on a topic that they really want to, that they like feel the need or like desire to explore. And
... See more‘ only the new of which one tires. One never tires of the old.’
Brooke Nemetz • We need to be more ritualistic

Bodies are Eating the World
Up from the ground comes a great swell of bodies. Running, lifting, bathing, shaking down, thinning out and waking up, bodies have taken over popular culture. Huberman is the biggest podcaster in the nation. One in eight Americans have tried GLP-1s. Seed oil discourse has created a new physical purity drive. Van der... See more
Up from the ground comes a great swell of bodies. Running, lifting, bathing, shaking down, thinning out and waking up, bodies have taken over popular culture. Huberman is the biggest podcaster in the nation. One in eight Americans have tried GLP-1s. Seed oil discourse has created a new physical purity drive. Van der... See more


