Imagination
The best practices and methods for cultivating imagination.
aron and
Imagination
aron and
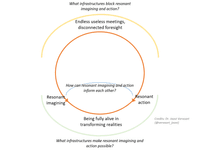
realisation.
We are asked to realise in three ways: as insight (get real) as self (become real) and as manifestation (make real). To realise what’s happening, who we are, and what we should do, we need to unlearn some things and reimagine others.
https://perspecteeva.substack.com/p/falling-in-love-with-the-discomfort
We take the profound power of conjuring new expressions, interpretations, and constructed worlds for granted.
