Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas
The hard part of computer programming isn’t expressing what we want the machine to do in code. The hard part is turning human thinking – with all its wooliness and ambiguity and contradictions – into computational thinking that is logically precise and unambiguous, and that can then be expressed formally in the syntax of a programming language.
The Future of Software Development is Software Developers
Consulting Slop
consultingslop.comAI discovered wholly new proteins before it could count the ‘r’s in ‘strawberry’, which makes it neither vaporware nor a demigod but a secret third thing.
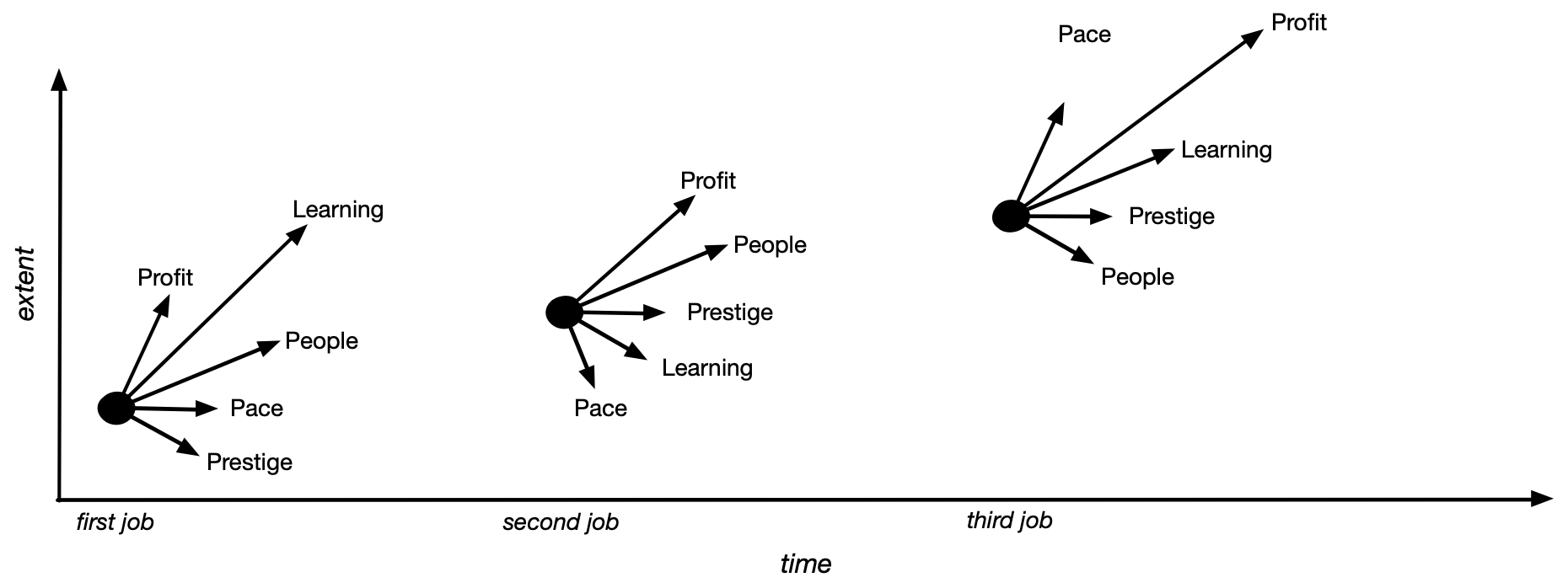
We all know “startups are hard,” but I think we tend to imagine that this difficulty is bounded, contained, modelable, a bit like running a marathon: yes, legs and lungs hurt, but that’s normal and appropriate, and we know the route, the distance, and that there’s a finish line. This is a kind of difficulty we can contend with without losing... See more
Chris Best • Principles and pragmatism
“If something is boring after two minutes, try it for four. If still boring, then eight. Then sixteen. Then thirty-two. Eventually one discovers that it is not boring at all.” ― John Cage
I’ve spent the last three years pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to conceive. I want more children, and I want close age gaps, and I want to write a book, and go to more parties, and keep publishing this newsletter. I still feel creative impulses, but they don’t always translate neatly to tangible output anymore. In fact, I would say they rarely... See more
Harling Ross Anton • My shrinking brain