Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas

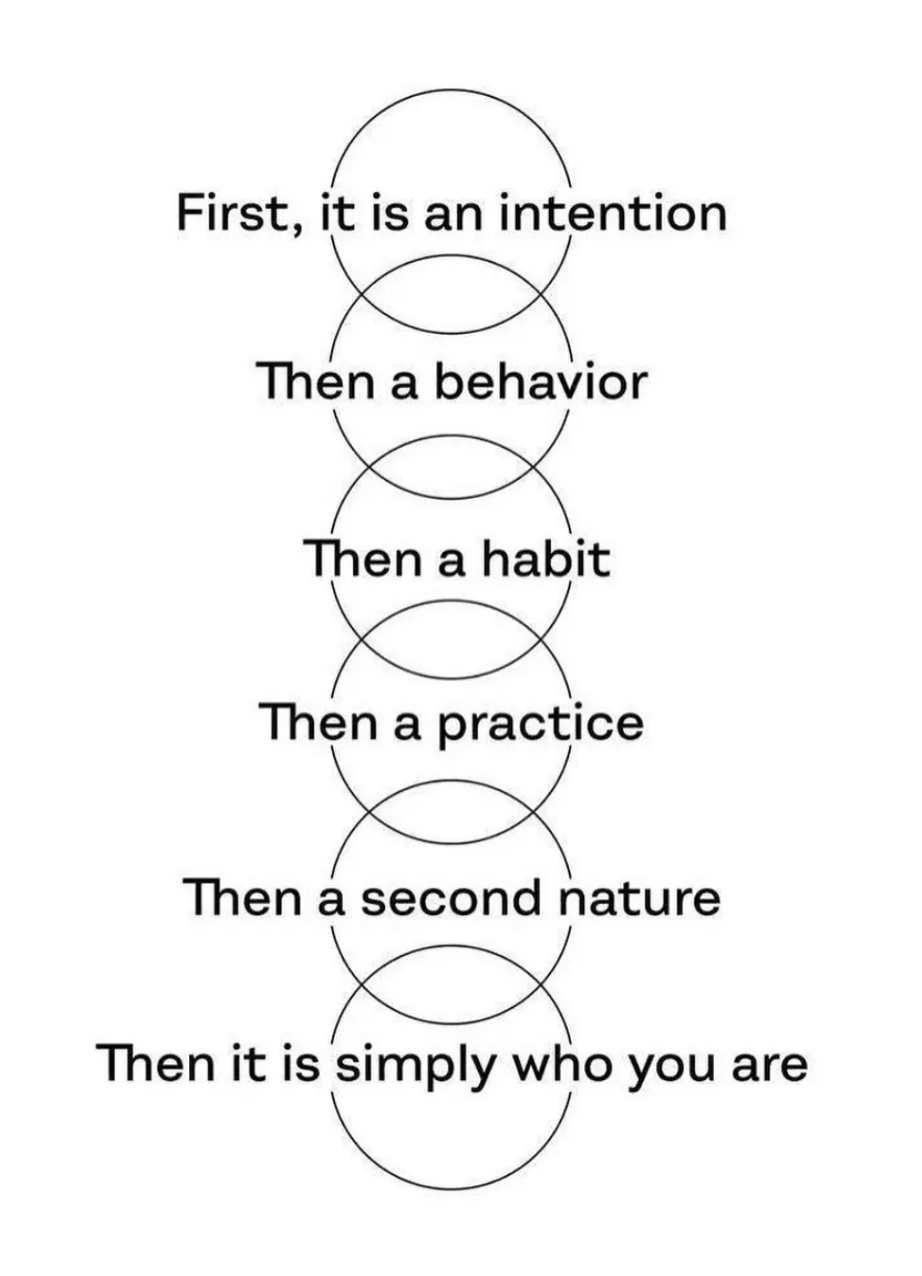
The Coherence Premium
joanwestenberg.com
I have a theory about nostalgia : It happens because the best survival strategy in an uncertain world is to overworry. When you look back, you forget about all the things you worried about that never came true. So life appears better in the past because in hindsight there wasn’t as much to worry about as you were actually worrying about at the... See more
Morgan Housel • A Few Things I’m Pretty Sure About


If you need a machine and don’t buy it, then you will ultimately find that you have paid for it and don’t have it. (Henry Ford via Clayton Christensen)
The trap of marginal thinking
No I.D. on Working with Common, Jay-Z, Kanye West and Being Humble | Red Bull Music Academy
youtube.comCreativity is the quality that you bring to the activity that you are doing. It is an attitude, an inner approach — how you look at things. Not everybody can be a painter — and there is no need also. If everybody is a painter the world will be very ugly; it will be difficult to live. And not everybody can be a dancer, and there is no need. But
... See more