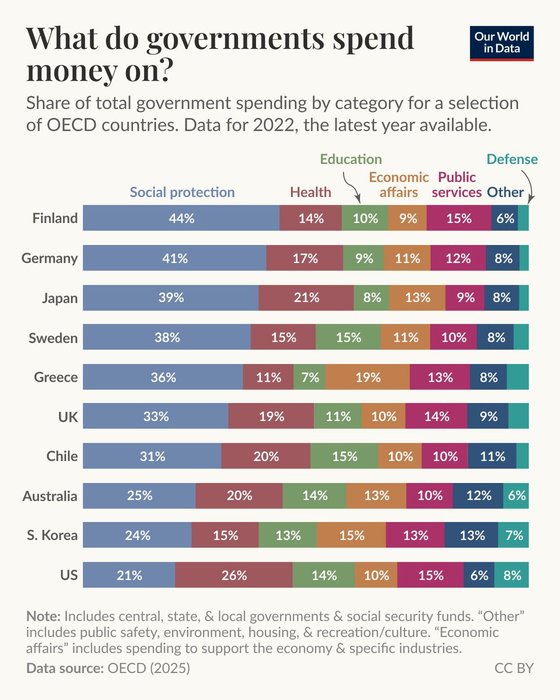
What do governments spend money on?
In the chart, we see spending in different categories, such as defense, health, and education, as a share of total government spending. This is shown for a selection of OECD countries.
For some categories, such as public services, the share... See more