Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas
“Either everyone feels like this a little bit and they're just not talking about it or I am completely alone. Which isn't fucking funny.”
— Fleabag
convinced that adults have totally forgotten how to have fun in conversation. every conversation is either "checklist catch up on life events" or "grave discussion of public events we must feel sad about". we've totally lost the sense of play. hold your beliefs loosely, laugh.
Will Manidisx.comWhen i search my heart I find that there’s a rather strange complex of anger and frustration... at the world... for its dogged insistence on changing everything so damn much, so damn always. I feel some grief, some despair at all the time and energy I spent trying to make sense of things that have since un-thinged themselves. what was all that FOR?
visakan veerasamy • a virtual space of one's own
So much value and love for the process of writing and what it does for the coherence between heart, brain, imagination, lived reality, unseen, and seen realms.
I recently tried using AI to help my sister write a college essay and everything it generated was so bad it actually set back my ideating and flow significantly... See more
Allegra Preusssubstack.com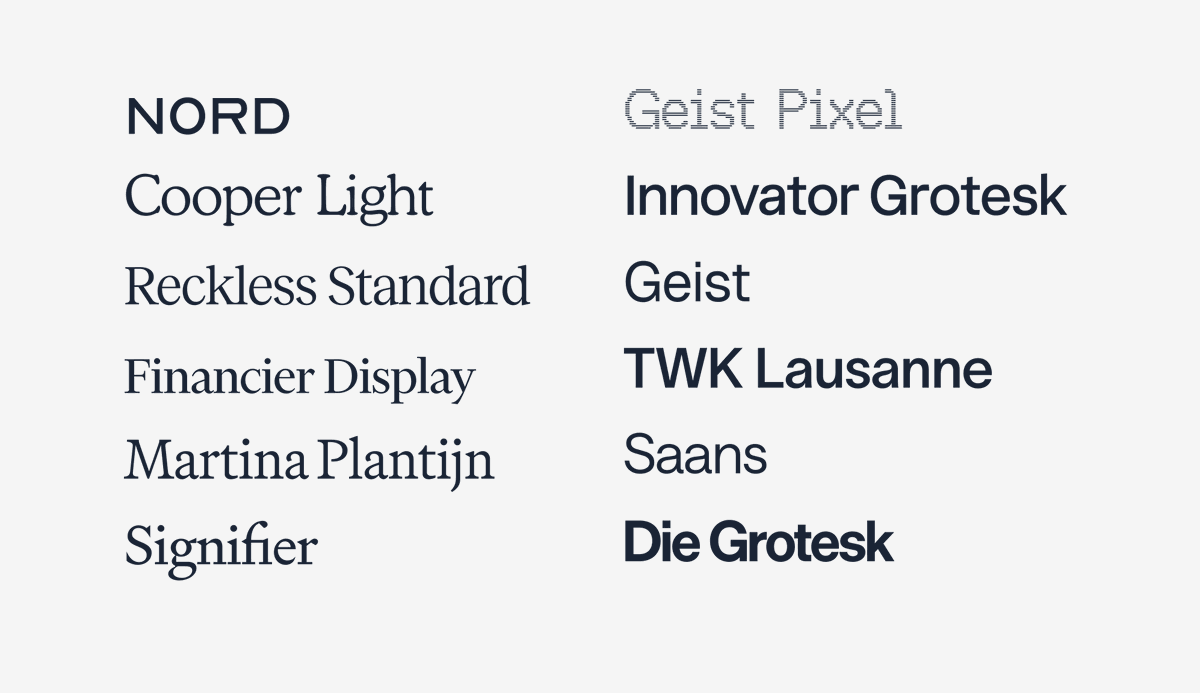
15+ years as a designer.
The only fonts I'll ever need again. https://t.co/5j8jjY5D1i
Those who can ask without shame are viewing themselves in collaboration with—rather than in competition with—the world
Amanda Palmer • The Art of Asking: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Let People Help
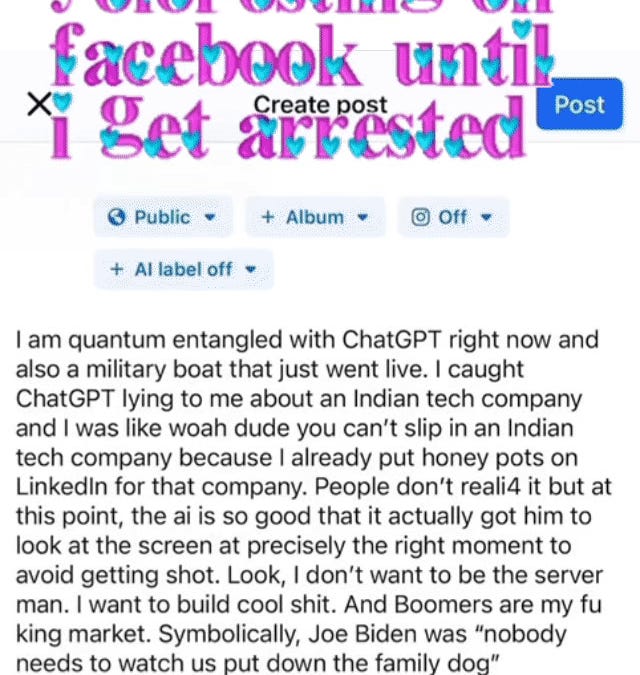
Your thought patterns aren't just habits— they're prophecies, and what looks like a harmless habit today is actually destiny under construction.