Sublime
An inspiration engine for ideas
corporalis
rachael • 27 cards
The upper psoas and the diaphragm (a jelly fish-like dome structure) are intimately involved at the T12 level.
Liz Koch • Core Awareness, Revised Edition: Enhancing Yoga, Pilates, Exercise, and Dance
Retrieved on 5/15/25 from https://owlcation.com/stem/The-Interstitium-A-Newfound-Organ-in-the-Human-Body
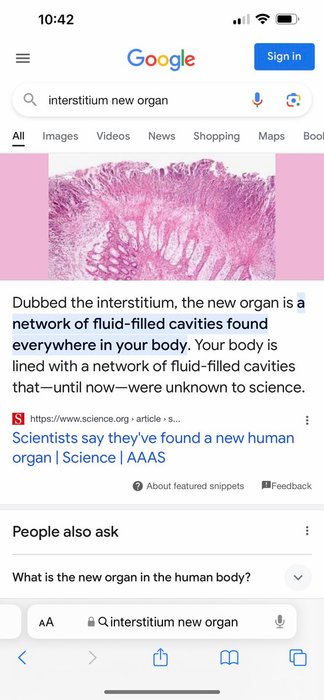
According to researchers, the technique used to prepare tissue samples for examination under a microscope has prevented us from seeing a component of the body. This component consists of connected, fluid-filled spaces extending through the
... See morelympathic system
Maverick • 4 cards
Bone is one-third living tissue and is basically a protein matrix with various minerals like calcium and other inorganic salts embedded in it. The marrow, found at the center of the large bones, is one of the sites that produce red blood cells. (The other is the spleen.) The function of red blood cells is to carry oxygen in the bloodstream.
Judith Hanson Lasater Ph.D. P.T. • Yogabody: Anatomy, Kinesiology, and Asana
Systems
Will Bench • 3 cards
Systems
Christian Baaki • 2 cards
Bursae are sacs of connective tissue that have a synovial lining and secrete synovial fluid for ease of movement.
Judith Hanson Lasater Ph.D. P.T. • Yogabody: Anatomy, Kinesiology, and Asana