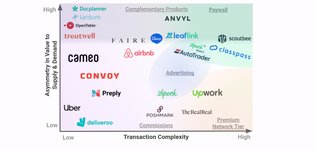
Asymmetry in value between demand and supply: Typically, the value created by a marketplace is asymmetrically distributed across participants. In other words, marketplaces are often more valuable for one type of participant— either the supply or demand side. However, the level of asymmetry is not consistent across marketplaces. For example, supply... See more