aron
@aronshelton
Designing and navigating various contextual arrangements with an enigmatic sense of hope. #wayfinder
aron
@aronshelton
“Because of the interconnectedness of all minds, affirming a plausible positive vision may be about the most sophisticated action any one of us can take.” -- Willis Harman
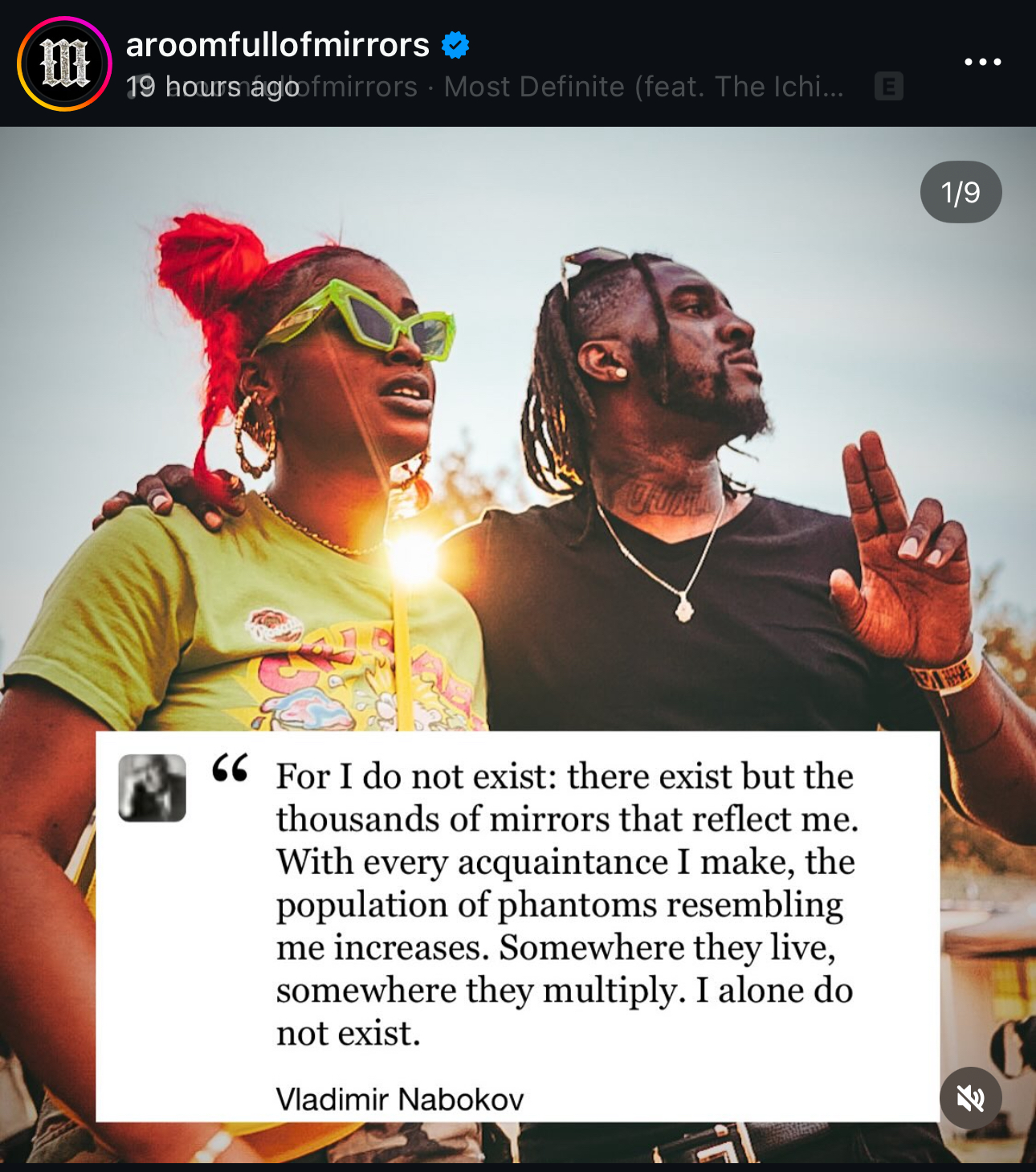
“Vibes are like the sun: we know that they exist, but we can't ever look at them directly. Concepts like community, mentorship, love, happiness, culture, education, progress, and paradigms are similarly resistant to hard definitions. Like the sun, we can feel their warmth, see them skittering around the periphery of our vision...but most of us know
... See moreLove this from Yancey Strickler:
An artist is a self-employed self-expressor.
A creator is a self-employed commercial expressor.